Explain Why Different Atoms of the Same Element Always Have
Arad which are attributes like weight density color smell etc. It has six protons six electrons and six neutrons so its atomic number is 6 and its relative atomic mass is 12.

6 P 2 1 Recognize That All Matter Is Made Up Of Atoms And Atoms Of The Same Element Are All Alike But Are Different From The At Atom Quantum Mechanics Nuclear
Daltons theory was soon widely accepted.

. A major activity of science is investigating and explaining causal relationships and the mechanisms by which they are mediated. 5 All the atoms of a given element are identical in every respect having the same mass size and chemical properties. Such mechanisms can then be tested across given contexts and used to predict and explain events in new contexts.
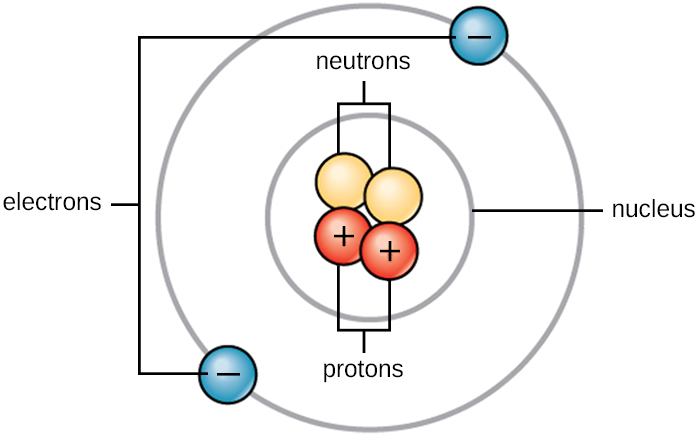
An atom with the same number of protons as another but a different number of neutrons An atom with the same number of electrons as another but a different number of protons The standard form of an element. Dimension 3 DISCIPLINARY CORE IDEASPHYSICAL SCIENCES. In the classical picture of an atom the electron revolves round the nucleus much like the way a planet.
The ordinary carbon we find in the world around us is sometimes called carbon-12. However it could not explain why atoms emit light of only discrete wavelengths. For example an isotope with 6 protons and 6 neutrons is carbon-12 or C-12.
Only the atoms of spatially extended bodies can be substances. The formal charge of an atom in a molecule is the hypothetical charge the atom would have if we could redistribute the electrons in the bonds evenly between the atoms. The atoms of the bodies are the carrier of accidents singl.
To complicate things a bit more we sometimes find atoms of a chemical element that are a bit different to what we expect. An isotope with 6 protons and 7 neutrons is carbon-13 or C-16. Atoms join together to form compounds.
Atoms of different elements are different and have different masses. M ost systems or processes depend at some level on physical and chemical subprocesses that occur within it whether the system in question is a star Earths atmosphere a river a bicycle the human brain or a living cell. However a small.
Most naturally occurring elements exist as isotopes. For example you could have carbon-14 and. In the cosmology of al-Asharî all immaterial things are considered accidents that inhere in a substance jawhar.
Most of it is still accepted today. How could an atom as simple as hydrogen consisting of a single electron and a single proton emit a complex spectrum of specific wavelengths. Atoms of the same element ie atoms with the same number of protons with different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes.
A given compound always consists of the same kinds of atoms in the same ratio. Atoms of the same element can have different numbers of neutrons however. Note the mass number of two isotopes may be the same even though they are different elements.
A nuclide is a species of an atom with a specific number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus for example carbon-13 with 6 protons and 7 neutrons. Events have causes sometimes simple sometimes multifaceted. In quantum physics organic chemistry and biochemistry the distinction from ions is dropped and molecule is often used when referring to polyatomic ions.
7 The number and kind of atoms in a given compound is fixed. The nuclide concept referring to individual nuclear species emphasizes nuclear properties over chemical properties whereas the isotope concept grouping all atoms of each element emphasizes. For example most hydrogen atoms have a single proton in their nucleus.
In the kinetic theory of gases the. A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds. Large-scale systems often have emergent properties that cannot be explained on the basis of.
Scale proportion and quantity. Another way of saying this is that formal charge results when we take the number of valence electrons of a neutral atom subtract the nonbonding electrons and then subtract the. All atoms of the same element are alike and have the same mass.
Depending on context the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. The only part. List the mass number of an element after its name or element symbol.
Take carbon for example. 6 Atoms of different elements differ in mass size and chemical properties.

Difference Between Atoms And Elements With Examples

Iv Isotopes 2 Or More Atoms Of The Same Element Having The Same Number Of Protons But Different Numbers Of Neutrons Atomic Theory Neutrons Atom
No comments for "Explain Why Different Atoms of the Same Element Always Have"
Post a Comment